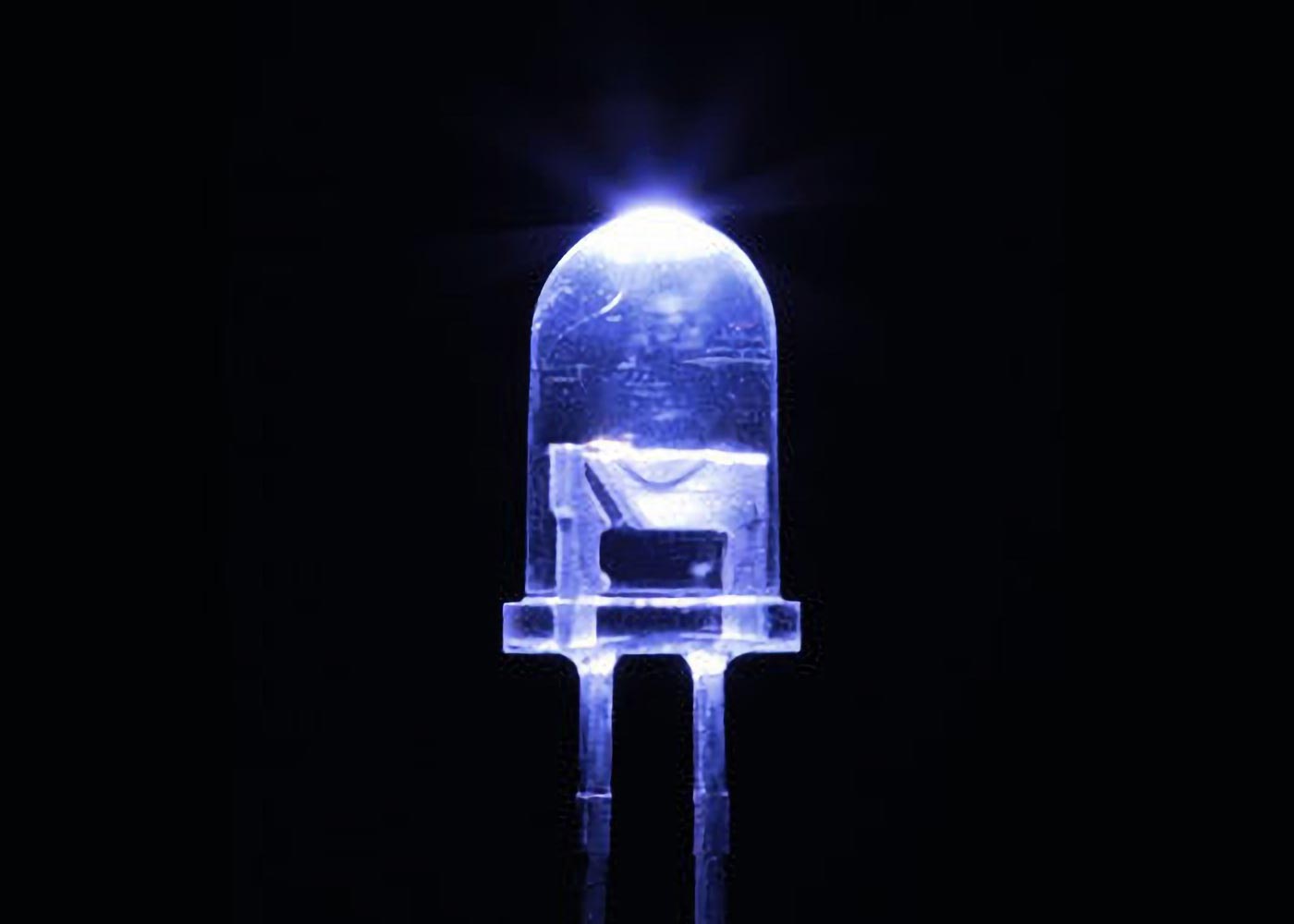
Малюнок 1. Більшість світлодіодів випромінюють видиме світло, але фізики RIKEN створили світлодіод, який випромінює у вузькій області далеких ультрафіолетових променів і є безпечним для людей, але смертельним для вірусів і бактерій. кредит: RIKEN
Потужна світлодіодна лампа може ефективно дезінфікувати поверхні, забезпечуючи безпеку людей.
Фізики RIKEN розробили високоефективну світлодіодну лампу, яка є протимікробною та противірусною, але безпечною для людини. Одного разу це може допомогти країнам вийти з тіні епідемій, знищуючи патогени в кімнатах, повних людей.
Ультрафіолетові бактерицидні лампи дуже ефективно знищують бактерії та віруси. Фактично, вони зазвичай використовуються в лікарнях для стерилізації медичних поверхонь та інструментів.

Масафумі Джо та двоє його колег розробили світлодіодну лампу, яка допомагає захистити суспільство від епідемій. кредит: RIKEN
Лампи такого типу можна створювати з використанням світлодіодів, що робить їх енергоефективними. Однак ці світлодіодні лампи випромінюють ультрафіолетове світло в шкідливому діапазоні[{” attribute=””>DNA and therefore cannot be used around people. The search is on to develop efficient LEDs that shine light within a narrow band of far-ultraviolet light that appears to be both good at disinfecting while remaining safe for people.
Germicidal LED lamps that operate in the absence of humans are often made from aluminum, gallium, and nitrogen. By increasing the amount of aluminum they contain, these LEDs can be modified to work in a wavelength region that is safe for humans. This approach has been used before but has resulted in dramatically reduced power.
To work through this issue, three physicists at RIKEN Quantum Optodevice Laboratory, Masafumi Jo, Yuri Itokazu, and Hideki Hirayama, created an LED with a more complex design. They sandwiched together multiple layers, each containing slightly different proportions of aluminum. In addition, in some layers they also added tiny amounts of silicon or magnesium.
This effectively created an obstacle course for electrons, hindering their movement across the material and trapping them for longer in certain areas. This resulted in an increased amount of light emitted by the device and a reduced amount absorbed by it.
The team used computer simulations to model all possible effects to help pin down the ideal design. “We then grew samples to see if it was effective or not,” Jo says. Precisely controlling the thickness of each layer was the biggest experimental challenge. They ended up with an LED operating in the far ultraviolet, with an output power almost ten times higher than their previous best.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought a new consciousness of the importance of being able to eradicate viruses and microbes on surfaces. “We trust that our findings and technologies will be very useful for safeguarding society against this and future pandemics,” says Jo.
Jo adds that the trio will strive to improve their LED’s performance even further. “There’s still much room for improvement in the output power and the power efficiency,” he notes.
Reference: “Milliwatt-power far-UVC AlGaN LEDs on sapphire substrates” by Masafumi Jo, Yuri Itokazu and Hideki Hirayama, 25 May 2022, Applied Physics Letters.
DOI: 10.1063/5.0088454

“Професійний вирішувач проблем. Тонко чарівний любитель бекону. Геймер. Завзятий алкогольний ботанік. Музичний трейлер”